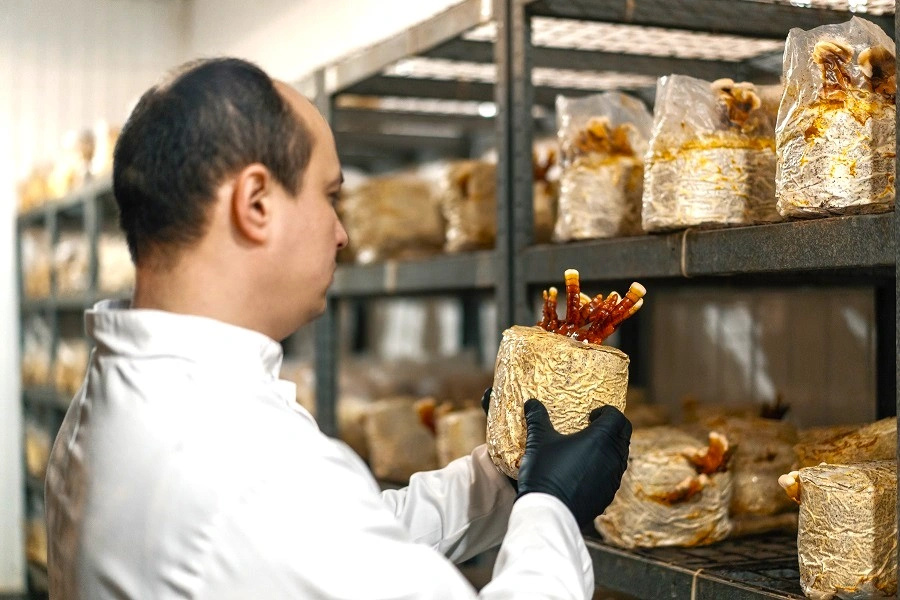
Functional mushrooms are gaining popularity, transitioning from niche capsules and powders to mainstream food and beverage options. Innovations include mushroom-infused coffee, energy drinks, chocolates, and gummies. As consumer interest grows in varieties like lion’s mane and reishi, industry advocates highlight the challenges regarding ingredient standardization, species differentiation, and the perception of functional mushrooms as a uniform category.
These unique fungi are celebrated not just for their nutritional value or taste, but also for their bioactive compounds that support various physiological functions, such as cognitive performance, immune system regulation, and metabolic health.
Notable varieties such as lion’s mane (Hericium erinaceus), reishi (Ganoderma lucidum), chaga (Inonotus obliquus), and cordyceps (Ophiocordyceps sinensis) are being increasingly recognized as “new-generation foods,” capturing consumer attention particularly in functional beverages.
According to surveys conducted by Innova Market Insights, over 25% of consumers worldwide express interest in functional mushrooms. Between 2018 and 2022, the introduction of new functional food and beverage products containing mushrooms surged by 22%, with North America contributing almost 49% of these new launches.
Food Ingredients First converses with the Functional Mushroom Council (FMC) and key North American growers and suppliers about the potential of functional mushrooms in mainstream food and beverages and why they should be recognized as scalable, scientifically-backed ingredient platforms instead of merely a niche supplement.
“Clear, category-level growth statistics and an increasing demand for multifunctional ingredients are propelling functional mushrooms into mainstream food and beverages,” states Dr. Julie Daoust, chair of FMC and chief science & technology officer at M2 Ingredients, North America’s leading functional mushroom producer.

Dr. Julie Daoust, FMC chair: Consumers now recognize lion’s mane before they even think of it as a mushroom.
The FMC was established last year to standardize practices and enhance transparency in the functional mushroom industry, which has faced scrutiny from consumer watchdogs regarding the validity of proposed health benefits.
“According to Grand View Research, functional mushroom food and beverage products reached approximately US$1.9 billion in 2025 and are anticipated to surpass US$2.2 billion by the end of 2026. This constitutes one of the fastest-growing segments, fueled by mushroom coffee and energy drinks within the larger functional ingredient ecosystem,” says Daoust.
“From a scientific perspective, mushrooms are gaining traction because they offer not just single-compound benefits. At M2 Ingredients, our full-spectrum functional mushrooms are characterized to contain over 5,000 bioactive and metabolite compounds linked to human health.”
Dispelling the Mushroom Myths
As consumer awareness of the health advantages of functional mushrooms expands, a significant challenge for the industry lies in the misconception that all functional mushrooms represent a single ingredient or benefit.
“The term ‘functional mushrooms’ actually encompasses thousands, if not millions, of unique species, each with its own metabolite profile, physiology, and health benefits. For instance, lion’s mane is primarily studied for cognitive health, reishi for immune support and stress reduction, cordyceps for energy enhancement, and chaga for its antioxidant properties,” explains Daoust.
Grouping these varieties under one umbrella term oversimplifies the science and complicates the pathway to effective standardization. While many mushrooms contain beta-glucans—compounds known for their immune and metabolic advantages—this commonality can further muddle distinctions between species.
The key to overcoming these challenges lies in stronger standardization and clearer communication. While mushrooms share certain components, each species holds unique chemistry that ultimately influences its effectiveness, application, and health benefits, as Daoust elaborates.

M2 Ingredients has developed solutions to enhance solubility and provide a more neutral flavor profile in functional mushrooms.
Several other challenges in the industry include solubility, flavor pairing, and sensory performance at the ingredient level. M2 Ingredients aims to address these issues at its new Center of Innovation, which recently opened in California.
Jay Schmalz, R&D Commercialization Manager and head of the new center, explains that the facility focuses on bridging the gap between the growing demand for functional mushrooms and the lack of specialized expertise to integrate them effectively into food and beverage systems.
“Our approach is to work backwards from the finished product, examining how functional mushrooms react under real processing conditions, including heat, pH levels, fat systems, liquids, fermentation, and shelf-life across formats like coffee, ready-to-drink beverages, powders, gummies, and bars,” Schmalz states.
The Center also seeks to dispel the false notion that mushrooms detract from taste or mouthfeel by demonstrating how these ingredients can be seamlessly integrated into “delicious, consumer-friendly products.”
Moving Beyond Supplement Hype
Incorporating functional mushrooms into everyday consumer habits is a pivotal step toward transcending the supplement market, as highlighted by Innova Market Insights’ fourth top trend for 2026, which indicates that consumers are gravitating toward beverages for functional health benefits.
“This shift is primarily driven by greater consumer interest in integrating functional benefits into existing daily routines rather than simply adding another pill to their regimen. Coffee, tea, and on-the-go beverages are natural frameworks for delivering benefits such as focus, energy, or immune support,” says Amir Karian, VP of Nutraceuticals at Monterey Nutra, a California-based company that cultivates high-quality mushrooms for extracts and powders.
“This trend has propelled functional mushrooms beyond niche offerings like mushroom coffee into a broader array of functional beverages. While initial mushroom coffees helped normalize the concept using blendable powders and light positioning, the category has rapidly diversified into ready-to-drink coffee and latte cans, sparkling teas, functional shots, and soda-like drinks.”

Functional mushrooms are incorporated into “better-for-you” chocolates, gummies, and snacks, making them feel more accessible than traditional supplements, according to Karian.
Beyond beverages, Karian highlights the significance of ingredient technology and innovation in formats that allow producers to respond to consumer preferences for “better-for-you” chocolates, gummies, and snacks—products that feel more accessible compared to conventional supplements.
“Earlier products often struggled with earthy flavors and gritty textures, which limited their appeal. Newer innovations focus on highly soluble extracts, smoother mouthfeel, and neutral taste profiles to align with specific beverage contexts like energy or relaxation.”
Functional Mushrooms: The Next Phase
Functional mushrooms have successfully entered the mainstream, surfacing in popular energy and focus beverages, such as Rockstar drinks containing lion’s mane, and functional offerings available at Taco Bell.
“What’s particularly exciting is that many consumers now recognize specific species names before acknowledging the broader category. For example, people often think about lion’s mane specifically before they realize it is classified as a mushroom,” notes Daoust.
Looking ahead, Daoust anticipates that a deeper biological understanding coupled with application-focused research, robust standards, and collaborative scientific efforts will help propel functional mushrooms beyond their current trend status.
In parallel, Erin Raser, director of Operations and Advocacy at Far West Fungi, asserts that to further integrate functional mushrooms into mainstream food and beverage products, enhancing U.S. grower capacity and establishing “transparent, reliable domestic supply chains” is essential.
She underscores the importance of investing in cultivation technologies, infrastructure, and research on high-yielding strains with proven medicinal profiles, in addition to seeking “expanded technical assistance and visibility from the USDA” along with supportive policy initiatives.
“Together, these efforts will empower U.S. growers, enhance transparency, and instill confidence in brands and consumers, encouraging the purchase of mainstream exotic and medicinal mushroom ingredients while bolstering the domestic economy.”