Copper’s Momentum: Key Catalysts to Watch in 2026
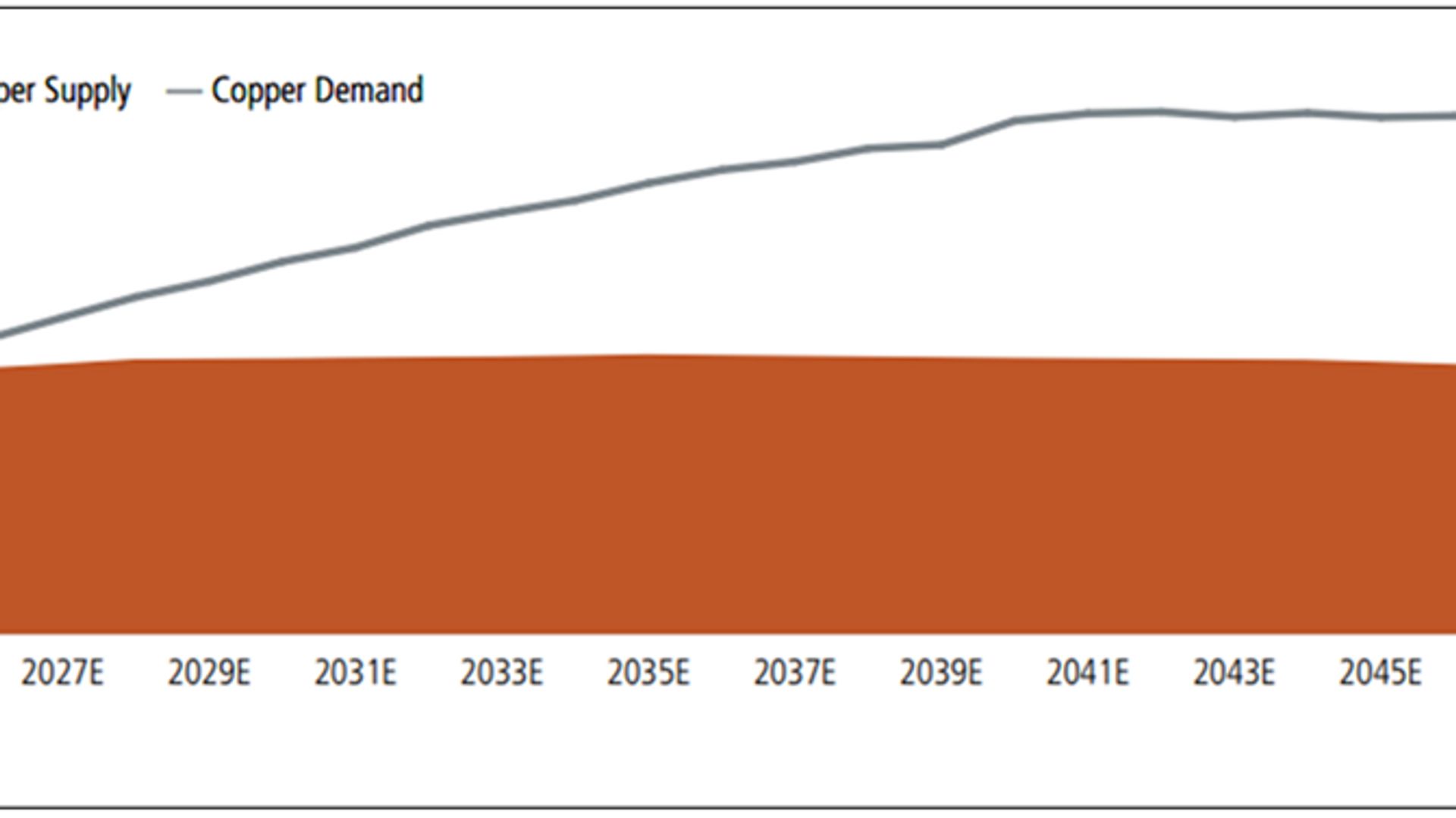
As the demand for copper continues to grow, particularly in green technologies and electric vehicles, understanding the factors that drive its momentum is essential. This article explores the critical catalysts that could shape the copper market in 2026, impacting both prices and supply.
1. Increasing Demand from Electric Vehicles
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is one of the most significant drivers of copper demand. Each EV requires an estimated 3 to 4 times more copper than a traditional gasoline-powered vehicle. As more consumers opt for electric transportation, the pressure on copper supply will intensify.
2. Renewable Energy Projects
As countries commit to reducing carbon emissions, investments in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro are on the rise. These projects often have high copper requirements, from wiring to infrastructure, further amplifying the metal’s demand.
Key Trends to Watch:
- Expansion of solar farms and wind turbines
- Government incentives for clean energy transition
- Growing public support for sustainability initiatives
3. Infrastructure Development
In many regions, aging infrastructure is in dire need of upgrades. Governments worldwide are investing in infrastructure projects, which often involve substantial use of copper for electrical systems, plumbing, and telecommunications. The potential for these developments to increase copper consumption is monumental.
4. Supply Chain Challenges
While the demand for copper is on the rise, supply chain disruptions can often hinder production. Factors such as labor strikes, geopolitical tensions, and environmental regulations can affect copper mining and processing operations worldwide. Keeping an eye on these challenges will be vital for anticipating market fluctuations.
Factors to Monitor:
- Mining regulations and legislation
- Global trade dynamics and tariffs
- Natural disasters affecting production
5. Technological Innovations
Advancements in mining technologies and recycling methods are set to change how copper is sourced and processed. Innovations can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve sustainability, potentially leading to a more stable supply in the future.
Conclusion
The outlook for copper in 2026 is promising, driven by significant catalysts such as the rise of electric vehicles, green energy projects, and infrastructure renewal. However, challenges such as supply chain disruptions must also be closely monitored. Keeping track of these factors will provide insights into the future of copper and its crucial role in a sustainable economy.