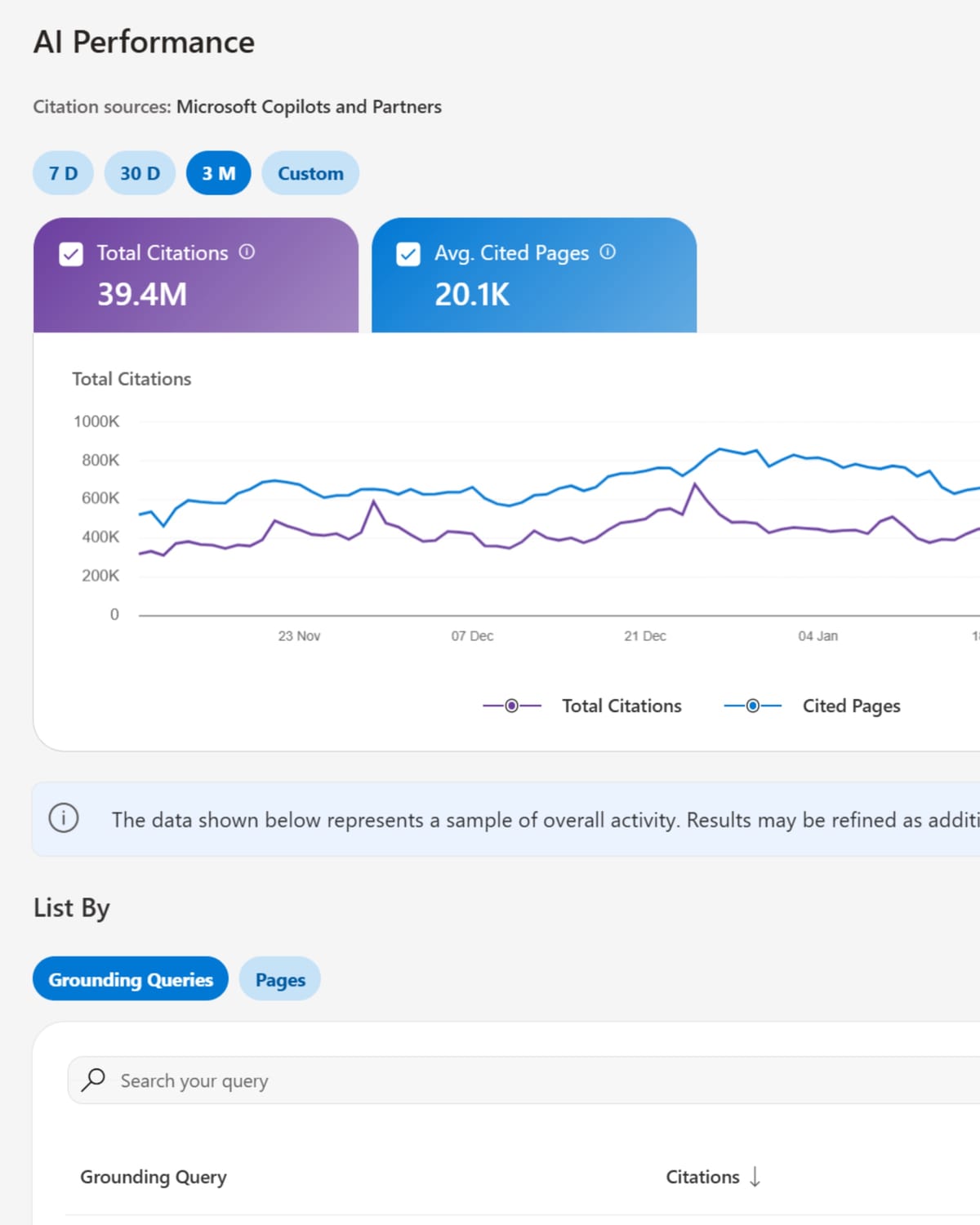
This week, Microsoft unveiled the AI Performance feature in Bing Webmaster Tools, a milestone that allows publishers to see how frequently AI systems reference their content across platforms like Microsoft Copilot, AI-generated summaries in Bing, and various partner integrations. Announced during a public preview on February 10, 2026, by Principal Product Managers Krishna Madhavan, Meenaz Merchant, Fabrice Canel, and Saral Nigam, this initiative marks Microsoft’s first significant push towards offering Generative Engine Optimization tools within its webmaster platform.
The dashboard arrives at a time when AI-driven search is transforming content discovery. Previously, publishers lacked clarity on whether their content appeared in AI-generated responses, leading to what industry experts have described as a “black box” for citation attribution. Microsoft’s new tools introduce transparency for the first time with four primary metrics that monitor citation frequency, page-level activity, grounding query phrases, and temporal trends.
As stated by Microsoft, the dashboard “shows where and how content from your site is referenced as a source across AI experiences.” This newfound clarity extends beyond traditional blue links to include citations in generative answers—an essential aspect for understanding today’s content performance. Following its extensive enhancements over 2025, AI Performance introduces a novel set of tools for generative search optimization.
This implementation offers publishers a total citation count that reflects how many times their content is utilized in AI-generated answers over specific time periods. While these counts illustrate reference frequency, they do not indicate where or how content is displayed within individual answers. Average cited pages provide insights into how many unique pages from a site are referenced each day across supported AI platforms, aggregating overall citation patterns.
Grounding queries reveal the key phrases that AI systems employ to retrieve referenced content. Microsoft acknowledges that this data offers only a sample of overall citation activity and intends to refine these metrics with additional data processing. Page-level citation activity allows users to identify which URLs receive the most references, facilitating the identification of frequently cited pages over selected date ranges. Additionally, the timeline visualization illustrates how citation activity evolves over time across supported AI experiences.
Microsoft has emphasized that Bing respects all preferences indicated by content owners via mechanisms like robots.txt. This commitment directly addresses the rising concerns among publishers regarding AI systems accessing content without explicit consent or compensation frameworks. The company positions this dashboard as a supplementary tool that enhances existing search performance metrics rather than replacing them.
Moving Beyond Traditional Search Metrics
The technical implementation of this dashboard significantly diverges from the conventional search performance reporting that Bing Webmaster Tools has traditionally provided. Citations in AI-generated answers function independently of metrics like click-through rates, impressions, or average positions that characterize standard search engine optimization strategies. A page may garner extensive citations without driving significant traffic, or it may generate traffic without a corresponding citation frequency.
This differentiation is important because AI-generated answers often fulfill user information needs without necessitating clicks to source websites. Research by PPC Land has shown that AI search visitors can have 4.4 times greater value than traditional organic search visitors when evaluated by conversion rates, even though total traffic may decline as these AI systems provide comprehensive information directly in responses.
The grounding queries metric offers valuable insights into how AI systems align content with user prompts. These phrases differ from traditional search keywords as they reflect AI retrieval logic rather than user-entered queries. By understanding which phrases trigger citations, publishers can better optimize content structure and depth for AI comprehension, moving beyond a focus solely on human readers or traditional search algorithms.
Microsoft’s documentation suggests that publishers utilize grounding query insights to identify which content frequently appears across AI answers and discover opportunities to enhance clarity, structure, or completeness on pages that are indexed but cited less often. The company regards citation frequency both as validation of current reference usage and as a means to uncover content performance patterns across generative experiences.
Content Optimization for AI Citation
Microsoft has provided specific recommendations for publishers aiming to boost citation frequency through improvements in content quality. The company advises enhancing depth and expertise, noting that pages cited for particular grounding query phrases frequently reflect a clear subject focus and domain authority. By expanding coverage in related areas, publishers can affirm authority signals that AI systems consider during source selection.
Improving structure and clarity through clear headings, tables, and FAQ sections helps surface key information, making it easier for AI systems to reference accurately. Supporting claims with evidence such as examples, data, and cited sources can enhance trustworthiness when content appears in AI-generated answers. Keeping content current through regular updates ensures that AI systems use the most accurate version of published materials.
Reducing ambiguity across formats by ensuring that text, images, and videos consistently represent the same entities, products, or concepts can enhance comprehension. Microsoft has directed publishers to detailed guidance on “Optimizing Your Content for Inclusion in AI Search Answers” for more comprehensive structural recommendations.
This optimization approach aligns with industry trends referred to as Generative Engine Optimization. This method focuses on leveraging citation opportunities within AI-powered tools, including ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Microsoft Copilot, through prompt matching, citation hooks, and topical clusters designed to increase the likelihood of AI systems referencing content when generating responses.
Analysis from PPC Land has emphasized that citation-worthy content must encompass specific, verifiable claims and fact-based statements rather than vague generalizations. AI systems analyze content in chunks instead of assessing entire pages, necessitating that publishers optimize individual sections to function as standalone information units when extracted by AI systems.
IndexNow Integration for Fresh Content
Microsoft has underscored the importance of maintaining accurate and timely content for AI citations through its IndexNow protocol. This real-time notification system helps ensure information remains fresh across search and AI experiences by alerting participating search engines whenever content is added, updated, or removed. By facilitating quicker discovery of content changes, IndexNow ensures that AI systems reference the most current versions of pages when generating answers.
The protocol has seen substantial uptake, with 60 million websites joining IndexNow daily and 1.4 billion URLs submitted each day as of October 2023. The application of IndexNow in conjunction with AI Performance reinforces Microsoft’s belief that real-time content freshness is vital for maintaining citation relevance.
Publishers who have not yet adopted IndexNow can find implementation guidance at indexnow.org. This protocol works alongside comprehensive XML sitemaps, which Microsoft has repositioned as crucial infrastructure for content discovery in AI-driven search environments. According to Microsoft’s August 2025 announcement, AI-assisted searches increasingly rely on structured signals like sitemap freshness, change frequency, and last modified dates compared to traditional crawling methods.
Local Business Visibility Considerations
For local businesses, Microsoft has highlighted that providing accurate business information becomes particularly vital when AI experiences deliver answers to location-based queries. The company has advised businesses to register with Bing Places for Business, allowing them to keep essential details like address, hours, and contact information up to date and in line for inclusion in AI-generated responses.
The revamped Bing Places for Business platform, launched on October 3, 2025, transitioned from bingplaces.com to bing.com/forbusiness, introducing new import features and tools. This free service enables businesses to create and manage listings that appear in Bing search results and Bing Maps, thereby enhancing visibility to prospective customers in search of local services.
Businesses can easily import their Google Business Profile listings for instant verification or create their Bing profile manually by adding or claiming their listing. The platform also supports bulk editing tools for managing multiple listings simultaneously, addressing scalability for businesses operating across various locations.
Competitive Positioning Against Google
The launch of AI Performance places Microsoft ahead of Google in delivering dedicated tools for AI citation visibility. While Google has extensively deployed AI Overviews throughout 2025, it has yet to release comparable analytics that show publishers how frequently their content appears in AI-generated summaries or which specific pages gain citations most often.
This competitive edge is crucial, as understanding AI citation patterns has become vital for publishers adapting to the shift towards generative search. Research documented by PPC Land has shown that citations from ChatGPT frequently reference content ranking in traditional organic search positions 21 or lower about 90 percent of the time, contradicting previous SEO assumptions about the correlation between ranking and visibility.
Microsoft’s broader AI strategy has integrated citation and grounding mechanisms across multiple products during 2025. The company’s Copilot advertising business surpassed $20 billion in annual revenue by April 2025, with search and news advertising revenue experiencing a 21 percent increase in recent quarters. Research compiled by Microsoft Advertising has shown Copilot achieving 73 percent higher click-through rates compared to traditional search advertising.
The AI Performance dashboard builds on Microsoft’s enhanced Bing Webmaster Tools capabilities, which have included the transition of the Recommendations feature replacing Insights in October 2024, the introduction of 24-month historical data retention announced in August 2025, and the limited preview of Copilot integration for real-time question answering, launched in October 2024.
Industry Implications and Future Development
The release of this dashboard signifies Microsoft’s commitment to enhancing transparency between AI systems and the open web, addressing longstanding concerns regarding attribution and visibility in AI-generated content. Publishers have long called for greater insight into how AI platforms utilize their material, particularly as traffic patterns increasingly shift from traditional link-based discovery to synthesized answers.
Marketing professionals are confronted with intricate optimization challenges as they navigate the balance between traditional SEO and evolving demands for AI citation. The four-layer framework documented by PPC Land categorizes contemporary search optimization into Answer Engine Optimization, Generative Engine Optimization, AI Integration Optimization, and Search Experience Optimization—each requiring unique strategies and technical implementations.
Citation worthiness has become a distinct optimization need, separate from traditional ranking factors. Content must feature specific, verifiable claims and fact-based statements rather than vague generalizations. AI systems assess content at the chunk level, not the page level, compelling publishers to ensure that individual paragraphs or sections provide comprehensive, contextual information that remains functional when extracted by AI systems.
Microsoft’s announcement of AI Performance arrives amid ongoing industry discussions about suitable compensation and attribution models for AI training data and citations. The company’s focus on adhering to robots.txt and other control mechanisms acknowledges publisher concerns about content utilization, although the dashboard itself centers on measurement, not monetization or licensing frameworks.
The public preview status of this feature indicates Microsoft’s intent to enhance and refine the tools based on feedback from webmasters. The company commits to ongoing collaboration with publishers and the webmaster community to improve inclusion, attribution, and visibility across both search results and AI experiences as the technology advances.
Publishers now have dedicated tools through Bing Webmaster Tools for gaining comprehensive insights into AI citation patterns, though the metrics currently represent early-stage implementations expected to evolve as Microsoft processes additional data and incorporates community feedback. The dashboard offers fundamental visibility into a rapidly changing content discovery landscape, where AI-generated answers increasingly mediate between users and original sources.
Timeline
Summary
Who: Microsoft’s Bing team, led by Principal Product Managers Krishna Madhavan, Meenaz Merchant, Fabrice Canel, and Saral Nigam, announced the AI Performance dashboard for publishers, webmasters, and SEO professionals managing websites indexed by Bing.
What: The AI Performance feature is a new addition to Bing Webmaster Tools that offers publishers insights into how their content is cited across Microsoft Copilot, AI-generated summaries in Bing, and select partner integrations. The dashboard tracks total citations, the average number of cited pages per day, grounding queries used by AI systems to retrieve content, page-level citation activity, and trends in citation over time.
When: Microsoft announced the public preview on February 10, 2026, marking the first availability of AI citation analytics within a major search engine’s webmaster tools.
Where: The AI Performance dashboard is available within Bing Webmaster Tools, where publishers can monitor indexing, crawl health, and search performance. The citations tracked cover Microsoft Copilot, AI-generated responses in Bing search results, and select partner integrations featuring Microsoft’s AI systems.
Why: As AI becomes an increasingly prevalent method for information discovery, visibility now extends beyond traditional blue links to encompass whether content is cited and referenced when AI systems generate answers. Microsoft developed AI Performance as an initial step toward Generative Engine Optimization tools in Bing Webmaster Tools, helping publishers gain insights on how their content is utilized in AI-driven experiences and offering guidance to boost citation frequency through content quality, structure, and freshness optimizations.
Share this article