Exploring Martian Mysteries: The Significance of the Black Beauty Meteorite
The quest to uncover the mysteries of Mars has captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike. One noteworthy discovery contributing to our understanding of the Red Planet is the Black Beauty meteorite, a remarkable piece of space rock that holds potential clues about water presence on Mars and the possibility of extraterrestrial life.
A Remarkable Discovery
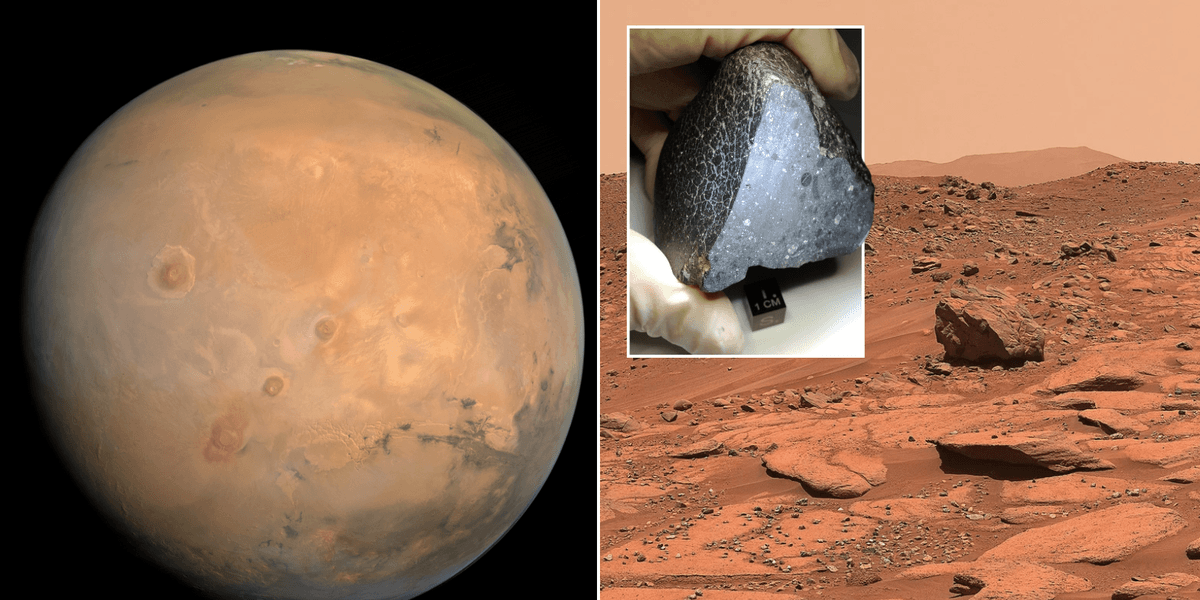
The Black Beauty meteorite, officially termed Northwest Africa 7034, weighs 320 grams and earned its nickname due to its unique appearance. Found in 2011 by nomads in the Sahara Desert, this meteorite is believed to have been propelled to Earth by a powerful impact on Mars. While the exact timing of its journey remains uncertain, researchers estimate that the oldest components of this meteorite date back around 4.5 billion years. Scientists have long been intrigued by its contents, especially after initial studies identified traces of water within the rock over a decade ago.
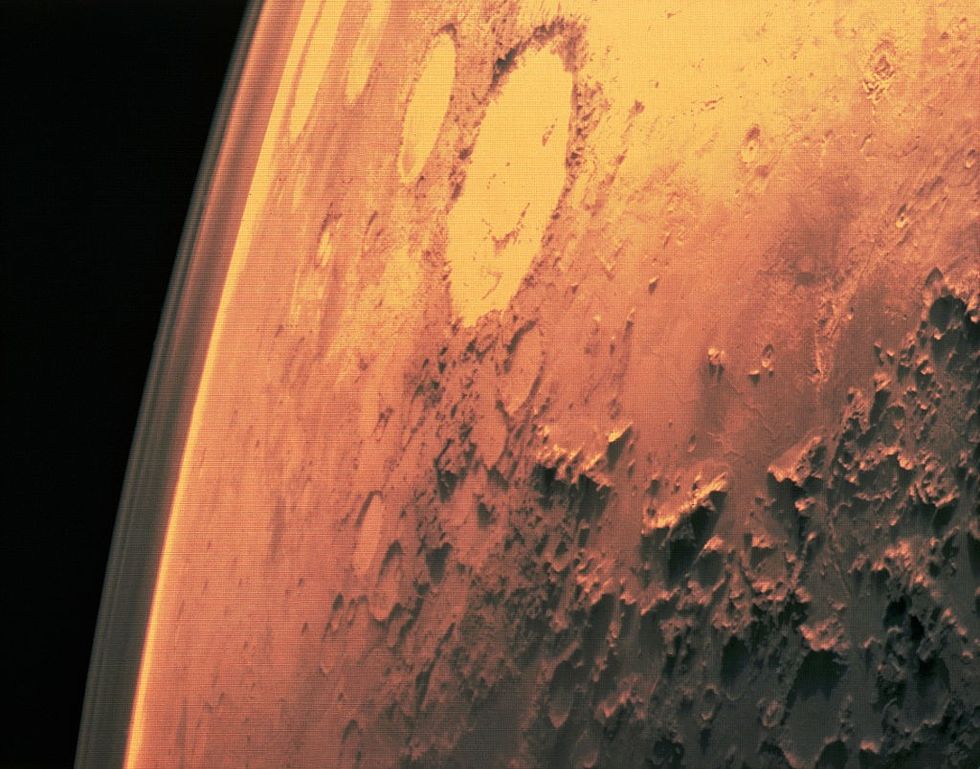

Researchers believe a powerful collision on Mars (pictured) sent the rock hurtling towards Earth | GETTY
New Insights Through Technology
Recent advancements in neutron scanning technology have shed light on the potential water content within the Black Beauty meteorite. The latest analysis revealed tiny particles of ancient water trapped inside, with new research suggesting that the water content exceeds earlier estimates. Scientists conducted this study on a small fragment of the meteorite, about the size of a fingernail.
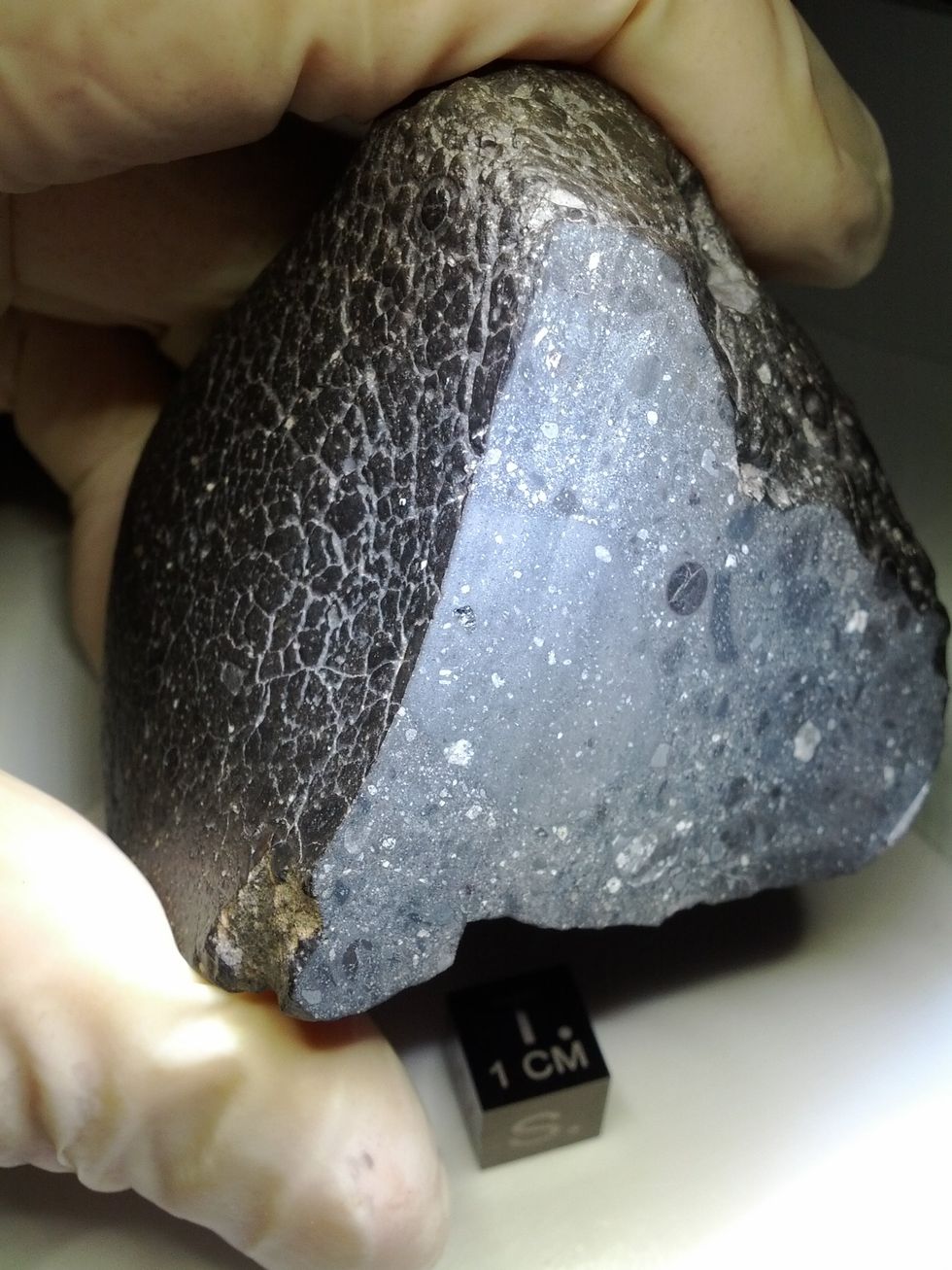

PICTURED: Northwest Africa 7034, nicknamed ‘Black Beauty’, which contains a tiny amount of water | NASA
This small sample was found to contain between 0.4 and 0.6 percent water, prompting researchers to further explore its implications. Water remains a fundamental focus for scientists investigating the existence of life beyond Earth, and their studies on Mars continue to reaffirm its significance as a potential habitable environment.
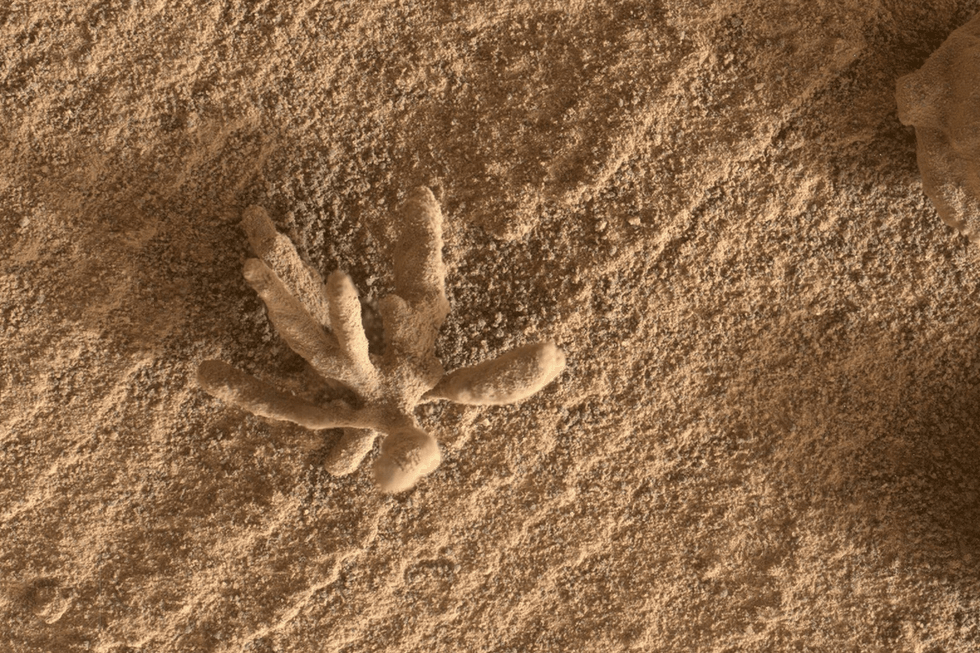

Last summer, new questions were raised over the possibility of life on the Red Planet after NASA’s Curiosity rover found a coral-shaped rock on its surface | NASA
Evidence of Ancient Oceans
Growing evidence suggests that Mars may have once harbored vast oceans akin to those on Earth. Recently, the Curiosity rover provided yet another intriguing find—a coral-shaped rock—which reignited speculation about the potential for life on Mars. As the rover, launched in 2011, continues its exploration, it has been capturing new images that fuel curiosity and academic inquiry into our neighboring planet.
Though NASA has recently scrapped plans to retrieve Martian rock samples directly due to high costs, the Black Beauty meteorite may represent the most feasible opportunity for researchers to investigate the potential for life on Mars in the foreseeable future.
Conclusion
The Black Beauty meteorite serves not only as a remarkable specimen of extraterrestrial origin but also as a crucial piece in the ongoing puzzle of Mars’ environmental history. As scientists continue to analyze its components, we inch closer to understanding the potential for life on the Red Planet and the role that water may have played in its past. This exploration of Mars not only enlightens our view of the universe but also challenges our perceptions of life’s possibilities beyond Earth.