In a complex and ongoing conflict, the electric war waged in Ukraine stands as a testament to what some analysts describe as Russian restraint, particularly under President Putin’s leadership. Early observations suggested that the Russian General Staff was keen on utilizing the campaign to target Ukraine’s energy grid and production facilities aggressively. However, as the situation has evolved, it has become evident that Russia has pursued a coalition war, strategically relying on the support of nations like China and India. This backing has inspired other countries in the Global South to resist U.S. and NATO sanctions while continuing to engage in trade with Russia. Notably, even as these nations have accepted Russia’s actions, there remains discomfort regarding the invasion of a neighboring country.
These geopolitical dynamics necessitated a more restrained approach from Russia in its military strategy, aiming to achieve its security objectives while minimizing military confrontations. This strategic choice may help mitigate resentments within Ukraine and even in Russia, where many individuals have familial ties to Ukraine.
In a recent assertive declaration directed at Europe, Putin stated that if hostilities are insisted upon, Russia is fully prepared to respond. He also indicated that Russia has not engaged in a large-scale war in Ukraine, suggesting that European nations are unaware of the true implications of their stance. Experts noted early in the conflict that it was unusual for Russia to preserve communication services rather than attacking cellular networks or broadcasting infrastructures. The cautious limitations in the electric war thus reflect broader strategic considerations.
By John Helmer, a distinguished foreign correspondent in Russia, independent journalist, former political science professor, and advisor to governmental leaders globally. Helmer served in the Carter administration and is uniquely positioned as an established journalist in Russia. Originally published at Dances with Bears

In a candid analysis of the General Staff’s electric war campaign since 2022, Vzglyad, a semi-official security analysis platform in Moscow, revealed that the sustained attacks on Ukrainian energy infrastructure had not achieved their intended military objectives due to the reticence stemming from Putin’s tit-for-tat strategy.
Yet, there appear to be shifts in this approach. Or have they?
Ukrainian military bloggers reported on December 23 that recent Russian military operations resulted in the complete de-energization of the Rivne, Ternopil, and Khmelnitsky regions. They warned of potential disconnections in Vinnytsia, Chernigov, Zhitomyr, Dniepropetrovsk, and Kharkov regions. Repair capabilities for damaged energy facilities are reportedly nearing exhaustion, raising questions about the impact of ongoing electric warfare operations.
Does this newly reported status imply that previous waves of electric war operations have cumulatively failed? A veteran military engineer specializing in electric warfare suggested, “Electrical spare parts arriving from Europe could have been halted. Key infrastructures, such as spare transformers and maintenance vehicles, could have been targeted effectively. Coordinated strikes could have overwhelmed Ukraine’s ability to carry out repairs promptly. Why hadn’t this strategy been employed sooner or more systematically?”
“Imagine if the main 33 electrical substations and associated towers had been destroyed during the autumn and winter of 2022-2023. What if the railways from Poland and Romania had been cut off? What if crucial transportation bridges had been targeted?”
“Unless those making decisions in the Kremlin lack intelligence—which is unlikely—the continuation of attacks without neutralizing the entire Ukrainian electrical system suggests a political motive: a conscious choice by President Putin.”
In an implicit acknowledgment, this perspective surfaced publicly for the first time on Tuesday in Moscow, particularly through a piece published by Vzglyad under the title “Zelensky’s stubbornness is finishing off the Ukrainian energy industry.” The report clarifies that the issue of stubbornness pertains not to Kiev but rather to Moscow.
Interestingly, unlike most Vzglyad articles, this one lacked cited sources, and no active writer has been found under the authored name, Nikolai Storozhenko. Instead, the name harks back to a notable literary historian from the 19th century, which invites readers to interpret this as a semi-official editorial.
For the full Russian original, click here.
By the end of 2025, Ukraine’s energy production capacity has been slashed by more than half, with residents of Kiev receiving electricity for an average of only 8 to 11 hours daily. This has severely impacted the Armed Forces of Ukraine and the broader economy. The situation has forced Ukrainians to direct blame solely at President Zelensky, as Russian strikes are framed as responses to his actions.
Initially, Ukraine’s energy infrastructure was not targeted; these attacks began later in 2022 following the Nord Stream pipeline explosions and assaults on the Crimean Bridge.
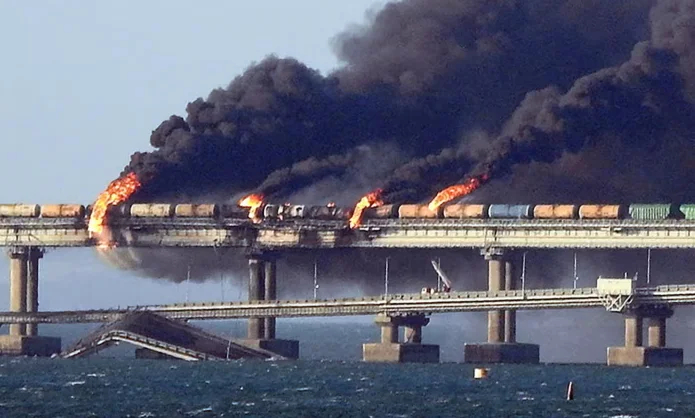

The first bombing of the Crimean Bridge on October 8, 2022, marked a turning point. The strikes initially targeted significant thermal plants, yet the impacts were limited, allowing Ukraine’s energy system to recover almost fully by late 2023.
Consequently, attacks on Ukraine’s energy sector continued into 2024 and 2025, evolving in nature due to Ukraine’s ongoing offensive against Russian oil refining. Among other reasons, these adjustments stemmed from elections ensuring that repaired facilities received some theoretical protection, albeit ineffective due to corruption. Moreover, energy production facilities were increasingly decentralized, supported by enhanced air defenses.
The crucial difference in 2025 is that this conflict has morphed into a comprehensive infrastructure war. Past strikes, while powerful, were individually aimed to compel compliance swiftly. As time progressed, targeting has shifted from power generation facilities to substations and power lines, which are critical for operational continuity.
Whereas thermal production could be interrupted without much systemic concern, significant challenges arise from Ukraine’s reliance on nuclear power plants, which are not easily assailable. However, taking consumers offline can lead to reduced nuclear output, opening up opportunities for alternative targets like hydroelectric plants.
The ongoing transition towards a systematic warfare approach means that recovery efforts for Ukraine’s energy systems have slowed significantly. By 2025, recovery costs escalated, shifting from $1.5-2 billion after 2022 strikes to an anticipated $3-4 billion in 2024 alone.
The Russian military command appears to have had the hope that Ukraine might relent; however, by late 2024, efforts to use energy infrastructure as leverage to negotiate peace yielded few results. Ukraine managed to navigate the subsequent heating seasons with minimal outages, undermining Russian strategic expectations.
The year 2025 has thus distinguished itself through heightened firepower. Significant increases in missile and drone numbers were recorded, correlating with reports of nearly 5,200 strikes from January to November, up from 4,500 in the previous year. Additionally, strikes have become more targeted, often focusing on one region to stretch air defense capabilities thin.
Throughout the year, Russia reported major operational outages, with over 70% of thermal power plants and 37% of hydroelectric plants effectively neutralized. This drop in energy capacity has had a direct correlation with Ukraine’s combat capabilities.
Despite increased energy imports, Ukraine’s energy infrastructure remains under strain, with daily electricity availability for Kiev residents plummeting again to 8-11 hours a day. These hours often coincide with late-night usage, translating into warnings of an impending energy catastrophe this winter amid dwindling repair resources.
An emerging trend in 2025 has been the intensification of strikes against Ukrainian gas production facilities. While such incidents were once sporadic, they have transitioned into systematic assaults designed to disrupt stockpiling efforts in preparation for winter, with damages escalating markedly from prior years.
The sustained onslaught on energy infrastructure has catalyzed significant migration away from Ukraine. In a six-week span during the autumn, the number of people leaving the country matched previous longer-term totals, contributing to further economic destabilization through labor shortages.
The energy crisis has contributed to inflation as Ukrainian businesses have seen electricity prices soar, forcing reliance on costly generators during power outages. Even budget-friendly generators yield rates well beyond official household pricing, leading to increased operational costs.
Furthermore, a select group of industries that manage to shield themselves from blackouts find protection costly, matching or exceeding European energy costs. Previously, access to affordable energy had fortified Ukraine’s competitiveness in global markets; however, the current reliance on generators drastically increases expenses, diminishing business viability.
As forecasts for Ukraine’s GDP growth deteriorate, evidence continues to mount regarding the detrimental influence of strikes against energy infrastructure. The IMF now forecasts much lower growth rates, raising questions about whether continued operational viability remains feasible for many businesses in Ukraine.
ANNUAL UKRAINE GDP MOVEMENT IN PERCENT, IMF CHART, INCLUDING 2025-26 FORECASTS
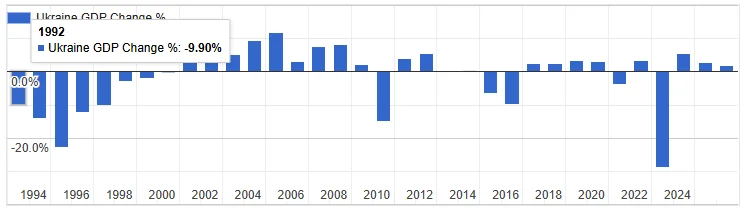
Source: Worldometers: Ukrainian GDP Data
WORLD BANK CHART FOR UKRAINE GDP, 1998-2024
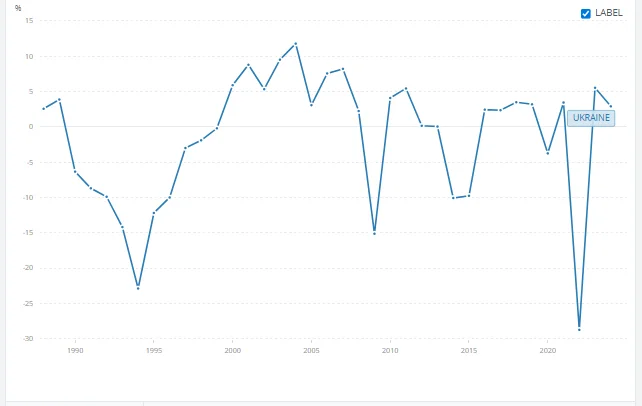
Source: World Bank: Ukraine GDP Trends
This pessimistic outlook is driven largely by energy costs and operational reductions stemming from ongoing strikes, raising critical questions about the sustainability of production activities in Ukraine.
Given the proximity of the European Union and its relative stability in energy and labor, discerning the primary factor leading to economic degradation—continued assaults on the energy sector or Zelensky’s unwavering approach—remains a pressing concern.
Recent news reports further illustrate this dilemma, showing that Trump’s team offered Zelensky an energy ceasefire in July, with assurances of compliance from Russia. His refusal, however, led to intensified Russian responses targeting the Ukrainian energy grid.
 Thus, Zelensky’s approach significantly impacts Ukraine’s GDP, which may ultimately be reflected in his political ramifications. His aggressive strategy towards Russian fuel infrastructure has compelled Russia to target the Ukrainian energy sector more decisively in 2025.
Thus, Zelensky’s approach significantly impacts Ukraine’s GDP, which may ultimately be reflected in his political ramifications. His aggressive strategy towards Russian fuel infrastructure has compelled Russia to target the Ukrainian energy sector more decisively in 2025.